
Anatomy Of Dog Skeleton With Labeled Inner Bone Scheme Vector
In dog skull anatomy, it is a short bone located caudally. Maxilla has a body and four processes. The external surface contains a prominent structure known as the infraorbital foramen. The medial surface has a nasal part that has numerous crests. Palatine Bone . Palatine bone is located caudomedial to the maxilla bone in the dog skull.
FileDog Skull.JPG Wikimedia Commons
In this video, I outline the main areas of the skull, using the dog as an example. Future videos will look at the individual bones and areas in more detail..

Chuck Does Art Canine Osteology Skull
Interesting Facts. Some cool facts about your dog's skull: Tiny holes in the base of the cranium are called foramina and are passageways for nerves and vessels. The big hole is where the vertebral column joins the base. The lines between the bones of the skull are called sutures. The skull is pretty thick, making dogs pretty "hard-headed ".

43 best images about Animal Anatomy on Pinterest
Dog skull, ribs, and sternum. It will be better if you read the dog skull anatomy, rib cage anatomy from the other article of anatomy learner. The dog skull, ribs, and sternum are also considered part of the axial skeleton. Here, I will provide a little information on the dog skull bones, ribs, and sternum.

Animal Anatomy and Anthropology. Runshaw Year 2
One extremely important part of a dog's skeletal anatomy is the skull. It is a long bone structure that encases the brain, and contains a cavity called the orbit, where the eye is located. It is elongated and extends to the end of the muzzle. Next comes the vertebra or spine. It is divided into five parts: the cervical, dorsal, lumbar, sacrum.
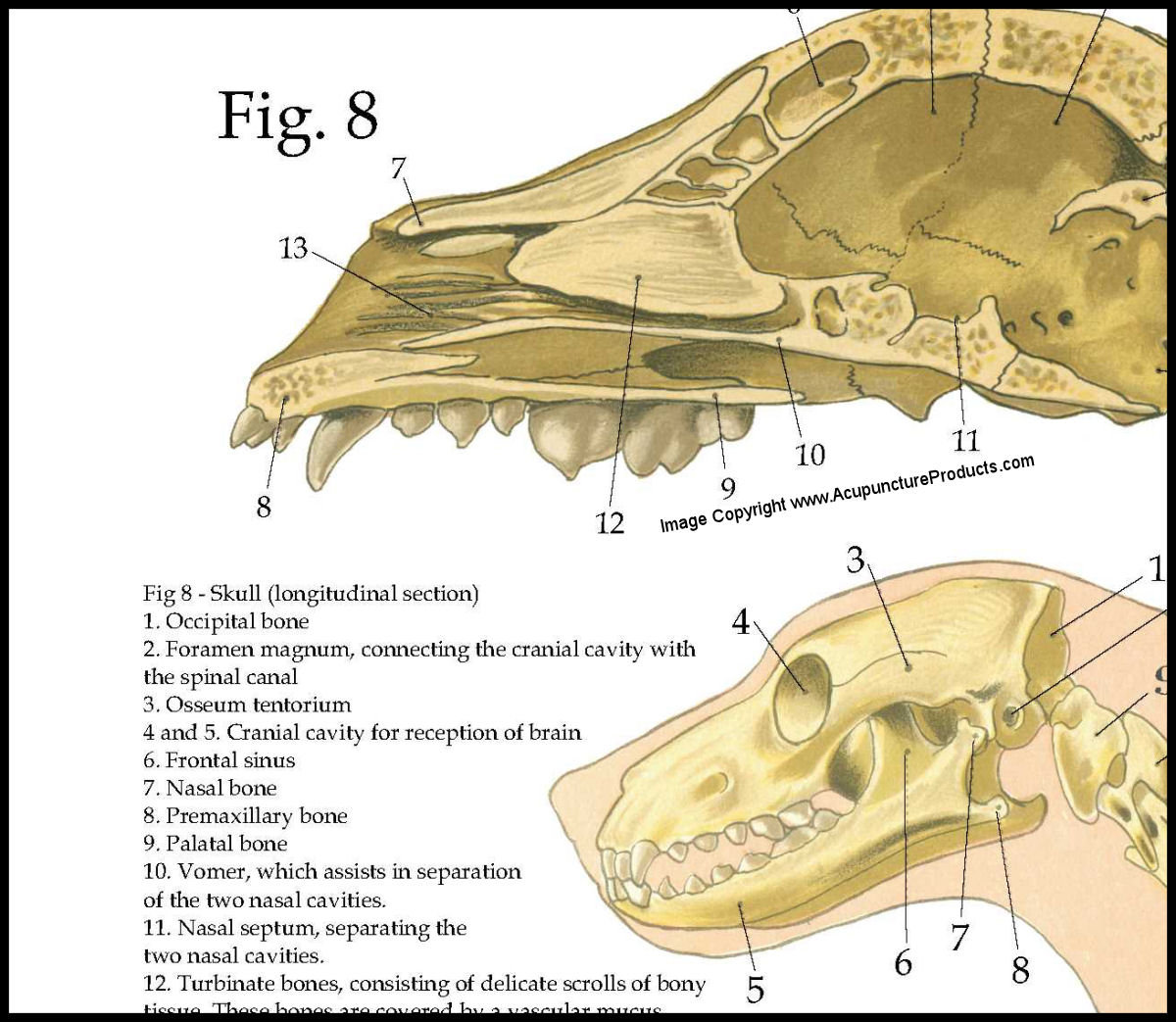
Dog Skeletal Skull Anatomy Poster 18 X 24 Etsy Australia
Learn about the anatomy (osteology) of the skull of a dog. Learn different bones that make up the skull and various ligaments attached to the skull.-----.

the anatomy of an animal's body and its external organs, including the
Dog Skull Anatomy. The main function of the skull in dogs and humans alike is to protect the brain. The interesting thing about dog's skulls is that they can be different shapes and sizes. Most breeds are categorized into the following dolichocephalic, mesocephalic and brachycephalic: Dolichocephalic - long headed such as the King Shepherd

Lateral Skull Anatomy Anatomical Charts & Posters
The SkullThe skull forms a rigid construction composed of many bones, which are mostly paired. It encompasses and protects the brain and the sensory organs o.

Dog skull anatomy animal 3D model TurboSquid 1472102
Maxilla bone from dog skull anatomy. The maxilla is a very short but highly caudal bone in dog skull anatomy. You will find a body and four different processes in the maxilla bone of a dog. The external surface of the maxilla bone of a dog has very prominent features, and that is the infraorbital foramen.
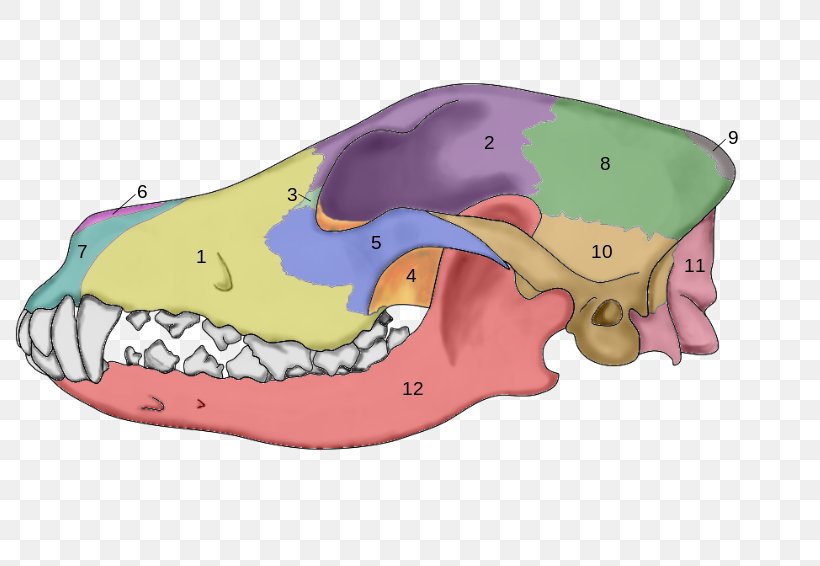
Dog Anatomy Skull Skeleton, PNG, 800x566px, Dog, Anatomy, Animal, Bone
The anatomy of the skull and nasofacial area of the dog and cat is complex, with cavities, sinuses, mandible, maxilla, dental arcades, and cranial cavity. In the 2-dimensional radiography image, the 3-dimensional skull creates a complex series of lines and superimposed osseous structures.
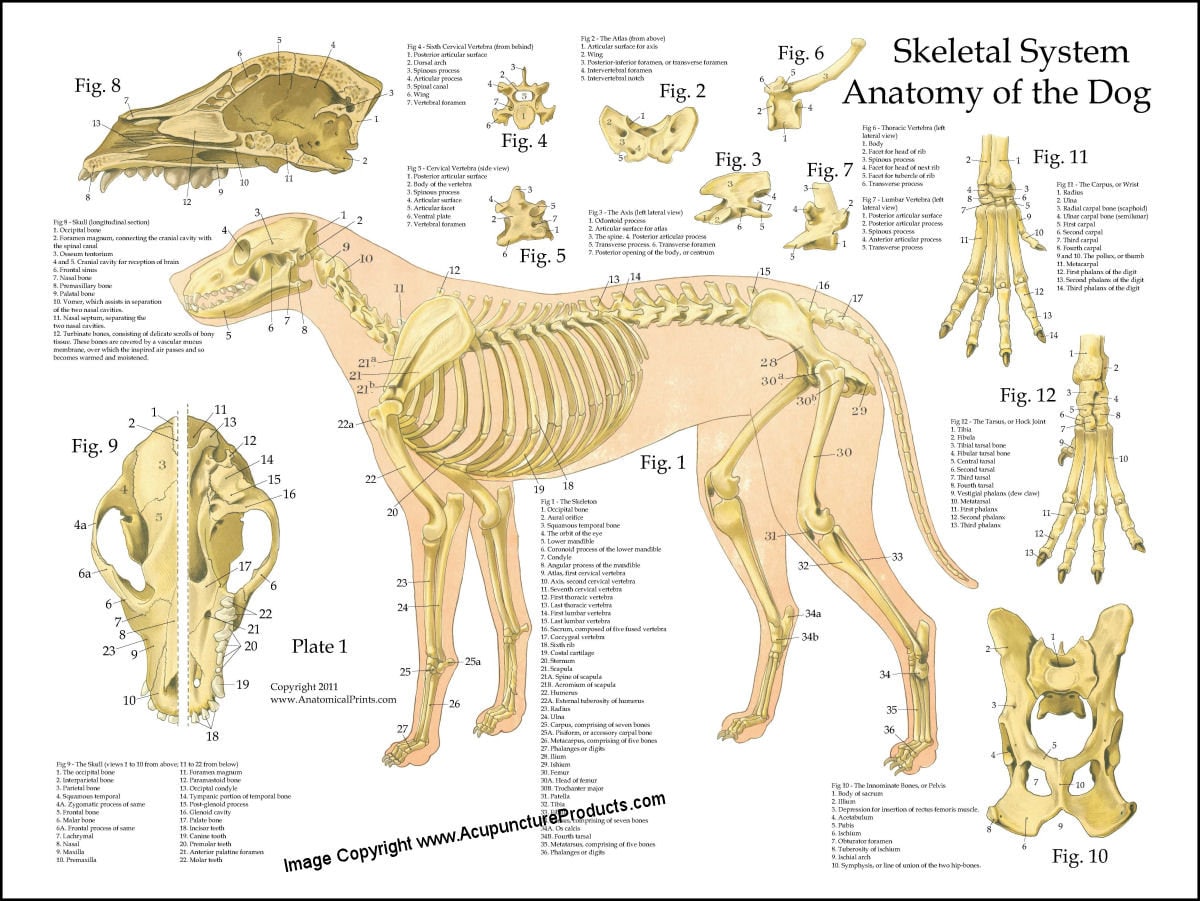
Dog Skeletal Skull Anatomy Poster 18 X 24 Etsy
The Mammalian Skull by Moore (1981) includes detailed descriptions of skull components, evolutionary changes, functional adaptations, and developmental anatomy. The bibliography is extensive. Hamon (1977) published a very detailed radiographic atlas of the dog skull.

realistic dog skull 3d model
The shape and size of the skull varies widely between different breeds of dog. Dogs have different skull lengths depending on breed. Mesocephalic dogs have average conformation whilst dolichocephalic dogs have longer skull lengths and brachycephalic dogs have shorter skull lengths. The skull protects the brain and head against injury and supports the structures of the face.

The skull of a dog. Structure of the bones of the head, anatomical
Dog anatomy comprises the anatomical studies of the visible parts of the body of a domestic dog.Details of structures vary tremendously from breed to breed, more than in any other animal species, wild or domesticated, as dogs are highly variable in height and weight. The smallest known adult dog was a Yorkshire Terrier that stood only 6.3 cm (2.5 in) at the shoulder, 9.5 cm (3.7 in) in length.

Dog skull anatomy basic and interesting Facts Dog skull, Dog anatomy
The anatomy of the dog is remarkably similar to that of a human in many respects, but there are also some very obvious differences, the main difference being in the shoulder assembly. In the human, the shoulder. The skull includes the brain case (back skull) and the facial area. While, in usual terminology, judges

The canine head and skull (CT) atlas of veterinary clinical and
Labeled anatomy of the head and skull of the dog on CT imaging (bones of cranium, brain, face, paranasal sinus, muscles of head) vet-Anatomy - Dog: Cranium - CT Cross-sectional anatomy - Head - CT Dog- Muscles: Anatomy atlas: Head, Face, Neck Cross-sectional anatomy - Sagittal: Nasal cavity, Tongue.

17 Best images about Dog Skeletal Reference on Pinterest Dog anatomy
Following overwhelming demand from our dedicated veterinary student community, we're thrilled to launch a brand-new series of captivating animations that bri.